There are more and less interesting options, but there are also clear favorites, if you look at the ratio of price and performance. And it seems that they should certainly include quad-core representatives of the Alder Lake family, belonging to the Intel Core ™ i3 series.

But this year, the Core i3 still moved to a more modern design: they jumped over the step and, like other members of the Alder Lake family, received the most advanced Golden Cove computing cores made using the new Intel 7 process technology. Thanks to this, the new Core i3- The 12300 and i3-12100 have significantly increased the performance level compared to their predecessors, although their nuclear formula has not changed – they have not received additional cores. But the best part is that the two steps taken at once in the microarchitecture did not become a reason for changing the positioning: the new Core i3 retained the usual recommended prices – $143 and $122, respectively (or $97 for the Core i3-12100F version without integrated graphics). And although in our situation the official prices have a rather distant relation to the real state of affairs, the Core i3-12300 and i3-12100 can still be bought for some sane money. And doing it right now can be a completely justified decision – as we will show below, they are far superior in performance to all alternatives presented in the same price segment.
However, the fact that the quad-core Alder Lake simply does not have worthy competitors is clear almost immediately. AMD tried to capture the quad-core segment two years ago by releasing the Ryzen 3 3300X with the Zen 2 architecture. However, it failed to supply the market with a sufficient number of such processors, and now they have almost completely disappeared from retail. And then the company generally considered this direction unpromising, and processors with four cores did not appear at all in the Ryzen 5000 series. Therefore, the new Core i3 will have to be compared first of all with higher-class solutions. In this review, which was prepared as part of a partnership project with Intel, we will see how the junior Alder Lake with four cores – the Core i3-12100 processor – compares to past six-core processors; answer the question whether four fast cores are enough for modern applications; and try to understand for what applications such a processor is best suited.
⇡#More about Core i3-12100
Although the Core i3-12100 belongs to the Alder Lake generation, it does not have much in common with flagship models like the Core i9-12900K. Of the sixteen cores, only four remained in it, there is no hybrid architecture at all, as well as Thread Director technology. In other words, according to the general principles of the internal structure, the new Core i3 are similar to the processors of the same series of the Comet Lake generation – they have four identical computing cores with Hyper-Threading support. But these cores in the Core i3-12100 have a progressive Golden Cove microarchitecture, that is, they are similar to the P-cores of the older Alder Lake.
If you just look at the formal specifications of the Core i3-12100 and do not go into details, it will seem like a close analogue of the Core i3-10100 – these processors have the same not only core formulas, but also clock frequencies. And in this sense, the new Core i3 are not like their older brothers: in the more expensive processors of the Alder Lake generation, the number of cores has increased compared to their predecessors. But there are quite understandable reasons for the stagnation in the Core i3 camp: there is no point for Intel to strengthen this series, because AMD has actually left the lower price segment. The introduction of 2020 Core i3 processors with four cores and Hyper-Threading technology was Intel’s answer to the Ryzen 3 3300X, and now there is simply nothing to answer. This means that the advantages of the Core i3-12100 over the Core i3-10100 are determined solely by the superiority of the Golden Cove microarchitecture over Skylake, which is actually not so small, because we are talking about a double microarchitectural step.
| Core i3-12100 | Core i3-10100 | Ryzen 3 3300X | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microarchitecture | Golden Cove | Skylake | Zen 2 |
| Technical process | Intel 7 | 14 nm | TSMC N7 |
| Socket | LGA1700 | LGA1200 | Socket AM4 |
| Kernels | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Threads | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Frequencies, GHz | 3.3-4.3 | 3.6-4.3 | 3.8-4.3 |
| TDP, W | 60 | 65 | 65 |
| MTP, Tue | 89 | 90 | 88 |
| L3 cache, MB | 12 | 6 | 16 |
| Memory | DDR4-3200 DDR5-4800 | DDR4-2666 | DDR4-3200 |
| Integrated Graphics | UHD 730 | UHD 630 | No |
| PCIe | 16 lines 5.0 4 lines 4.0 |
16 lines 3.0 | 24 lines 4.0 |
| Price (stated by manufacturer) | $122 | $122 | $120 |
However, studying the above table, it is easy to notice another useful feature of the Core i3-12100: in comparison with the previous quad-core, it has twice the L3 cache. And this is good in itself – in some applications, especially gaming, a large cache can cause a noticeable increase in performance. At the same time, the Ryzen 3 3300X has an even larger L3 cache, but it is built on the old Zen 2 microarchitecture, which, in terms of specific performance, was inferior to Cypress Cove, not to mention the more modern Golden Cove microarchitecture.
The Core i3-12100 processors are based on the same stripped-down semiconductor die used in some of the lower Core i5 processors – it has six cores and has an area of 162 mm2. At the same time, two cores are disabled, which, combined with relatively low operating frequencies, allows the Core i3-12100 to remain within the 60-W TDP. Thus, with a full multi-threaded load, this processor is able to operate at the maximum possible frequency of 4.1 GHz for an arbitrarily long time, and with a load on one core, its frequency rises to 4.3 GHz.
This can be confirmed by graphs of CPU power consumption, where we compare the Core i3-12100 with other quad-core core i3-10100 and Ryzen 3 3300X. The measurements were carried out in the game Horizon Zero Dawn and with resource-intensive multi-threaded rendering in Blender.
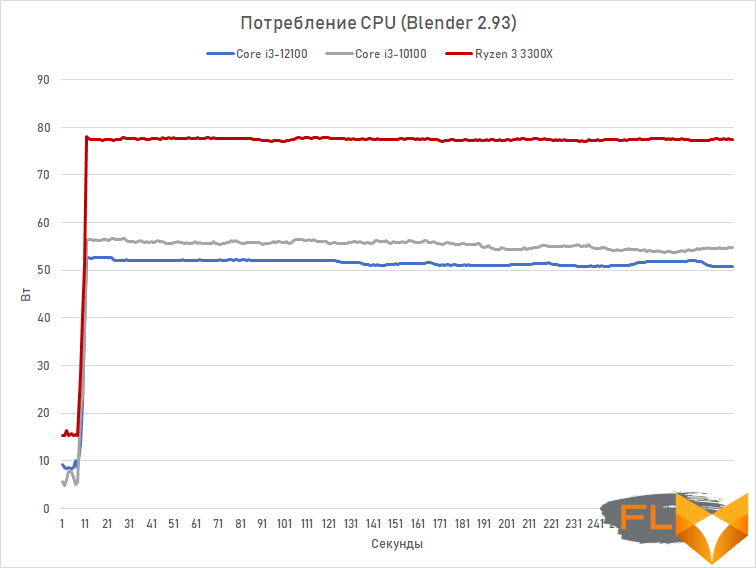
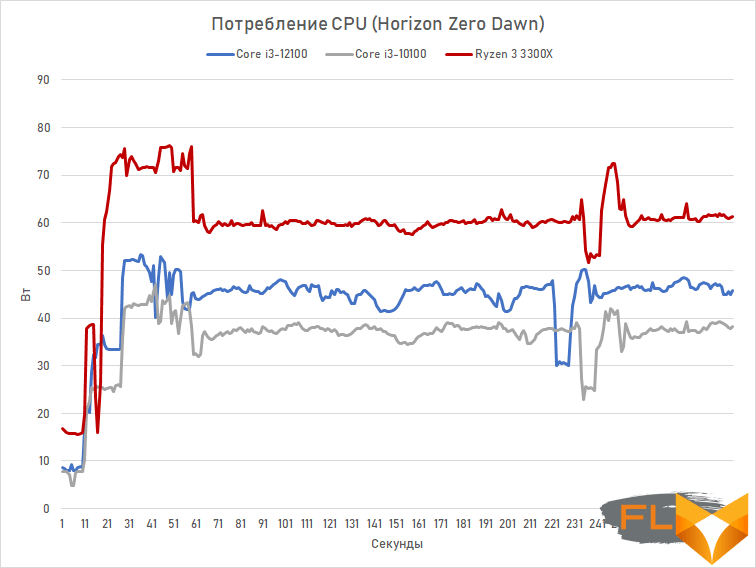
It is easy to see that the maximum power consumption of the Core i3-12100 is only 52 watts. And in average loads (in games), it generally consumes about 45 watts. These are quite small values, and, therefore, both budget motherboards based on the H610 chipset and simple cooling systems are suitable for it. For example, the standard Laminar RM1 cooler from the box is perfectly combined with this processor.

How such a cooler works in conjunction with the Core i3-12100 can be estimated from the processor temperature graph observed when rendering in Blender – in one of the most resource-intensive tasks.
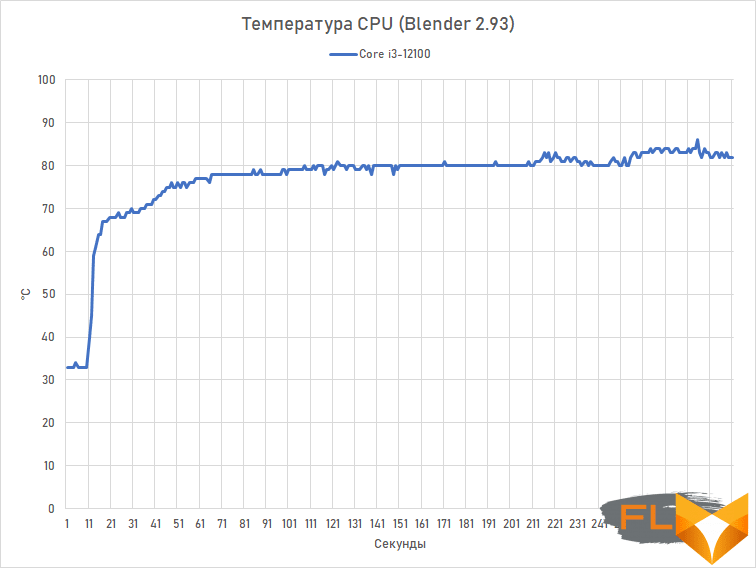
Even a seemingly unassuming cooling system keeps temperatures below the 85-degree mark. Therefore, it is really quite possible to save money on a cooler for the Core i3-12100. The only thing we should not forget is that its mount must be compatible with LGA1700, that is, it must be designed for the arrangement of holes in the board with a square with a side of 78 mm.
However, if you decide to save on the motherboard and choose a model based on the H610 chipset, then such a motherboard will deprive you of the possibility of overclocking RAM – this point must be borne in mind. However, in the case of the Core i3-12100, it is hardly worth worrying about this, since there are restrictions on memory overclocking in the processor itself. It does not allow increasing the VCCSA voltage (voltage on the system agent), which limits the stability of the memory controller in Gear 1 mode. Therefore, faster DDR4 memory modules than DDR4-3200, with some Core i3-12100 instances, may not work at all in synchronous mode on any motherboard, and with them you will have to activate the slow and unprofitable half-frequency mode of the Gear 2 memory controller.
If necessary, a system with a Core i3-12100 can be used without a discrete graphics card – this processor has a UHD Graphics 730 graphics core with 24 actuators. But you need to understand that these graphics are office-level, their 3D performance is not so high and will not allow you to comfortably play modern games even at 720p resolution. However, esports games like League of Legends, Fortnite or Valorant are still quite capable of it.
If there is no need for an integrated graphics core, then the Core i3-12100 has an analogue without this functionality – the Core i3-12100F. The choice of such a modification of the processor will save a lot of money – at the official price it is $25 cheaper.
⇡#Description of the test system and testing methodology
As already mentioned, the Core i3-12100 currently has no direct competitors, so the old quad-core Core i3-10100 and Ryzen 3 3300X processors were involved in the comparison with it. In addition, we have not forgotten about the six-core and six-thread Ryzen 5 3500X, which can still be found on sale at a relatively low price. The rest of the test participants are obviously higher class processors, surpassing the Core i3-12100 both in the number of cores and in the number of executable threads. Nevertheless, a comparison with them is still of some interest, since the Golden Cove microarchitecture makes the cores of the quad-core Alder Lake more powerful than the cores of processors of all other families.
- Processors:
- AMD Ryzen 5 5600X (Vermeer, 6 cores + SMT, 3.7-4.6GHz, 32MB L3);
- AMD Ryzen 5 3600 (Matisse, 6 cores + SMT, 3.6-4.2GHz, 32MB L3);
- AMD Ryzen 5 3500X (Matisse, 6 cores, 3.6-4.1GHz, 32MB L3);
- AMD Ryzen 5 3300X (Matisse, 4 cores + SMT, 3.8-4.3GHz, 16MB L3);
- Intel Core i5-12600K (Alder Lake, 6P+4E-cores + HT, 3.7-4.9/2.8-3.6GHz, 20MB L3);
- Intel Core i5-12400 (Alder Lake, 6P cores + HT, 2.5-4.4GHz, 18MB L3);
- Intel Core i5-11400 (Rocket Lake, 6 cores + HT, 2.6-4.4 GHz, 12MB L3);
- Intel Core i5-10400 (Comet Lake, 6 cores + HT, 2.9-4.3 GHz, 12MB L3);
- Intel Core i3-12100 (Alder Lake, 4P cores + HT, 3.3-4.3GHz, 12MB L3);
- Intel Core i5-10100 (Comet Lake, 4 cores + HT, 3.6-4.3 GHz, 6MB L3).
- CPU cooler: Noctua NH-D15S.
- Motherboards:
- ASUS ROG Strix B660-F Gaming WiFi (LGA1700, Intel B660, DDR5 SDRAM);
- ASUS ROG Strix X570-E Gaming WiFi (Socket AM4, AMD X570);
- ASUS ROG Strix Z590-A Gaming WiFi (LGA1200, Intel Z590);
- ASUS ROG Strix Z690-A Gaming WiFi D4 (LGA1700, Intel Z690, DDR4 SDRAM);
- ASUS ROG Strix Z690-F Gaming WiFi (LGA1700, Intel Z690, DDR5 SDRAM).
- Memory:
- 2x16GB DDR4-3600 SDRAM, 16-18-18-38 (Crucial Ballistix RGB BL2K16G36C16U4BL);
- 2x16GB DDR5-6000 SDRAM, 38-38-38-76 (G.Skill Trident Z5 RGB F5-6000U4040E16GX2-TZ5RK).
- Video Card: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 Founders Edition (GA102, 1395-1695/19500MHz, 24GB GDDR6X 384-bit).
- Disk subsystem: Intel SSD 760p 2TB (SSDPEKKW020T8X1).
- Power supply: Thermaltake Toughpower DPS G RGB 1000W Titanium (80 Plus Titanium, 1000W).
All compared processors were tested with canceled artificial consumption restrictions. This means that the PPT limits (for the AMD platform) and PL1/PL2 (for the Intel platform) are ignored, instead the maximum possible frequencies are used in order to obtain maximum performance.
The memory subsystems were configured using XMP profiles. LGA1200 and Socket AM4 processors were tested with DDR4-3600, and Alder Lake with DDR4-3600 and DDR5-6000.
The tests were performed on a system with the fastest GeForce RTX 3090 graphics card so that the performance of the graphics subsystem did not limit the speed of the compared processors from above, and the results obtained in gaming applications illustrated the maximum capabilities of the CPU as much as possible, and nothing else.
Testing was performed on the Microsoft Windows 11 Pro (21H2) Build 22000.282.0 operating system with KB5005635 and KB5006746 updates installed and using the following driver set:
- AMD Chipset Driver 3.10.08.506;
- Intel Chipset Driver 10.1.18838.8284;
- Intel SerialIO Driver 30.100.2105.7;
- Intel Management Engine Interface 2124.100.0.1096;
- NVIDIA GeForce 511.23 Driver.
Description of the tools used to measure computing performance:
Comprehensive benchmarks:
- Futuremark PCMark 10 Professional Edition 2.1.2508 – testing in Essentials scenarios (typical work of the average user: launching applications, surfing the Internet, video conferencing), Productivity (office work with a word processor and spreadsheets), Digital Content Creation (creating a digital content: photo editing, non-linear video editing, rendering and visualization of 3D models).
- 3DMark Professional Edition 2.22.7336 – testing in the CPU Profile 1.1 scenario with eight active threads and at the maximum possible processor load.
Applications:
- 7-zip 21.02 – archiving speed testing. The time taken by the archiver to compress a directory with various files with a total volume of 3.1 GB is measured. Uses LZMA2 algorithm and maximum compression ratio.
- Adobe Photoshop 2021 22.4.3 – Graphics performance testing. The average execution time of the Puget Systems Adobe Photoshop CC Benchmark 18.10 test script, which simulates the typical processing of an image taken by a digital camera, is measured.
- Adobe Photoshop Lightroom Classic 10.3 – Performance test for batch processing of a series of RAW images. The test scenario includes post-processing and export to JPEG at a resolution of 1920 × 1080 and a maximum quality of two hundred 16-megapixel RAW images taken with a Fujifilm X-T1 digital camera.
- Adobe Premiere Pro 2021 15.4.0 – performance testing for non-linear video editing. Measures rendering time to YouTube 4K for a project containing HDV 2160p30 footage with various effects applied.
- Blender 2.93.5 – testing the speed of the final rendering in one of the popular free packages for creating three-dimensional graphics. The duration of building the final model pavillon_barcelona_v1.2 from Blender Benchmark is measured.
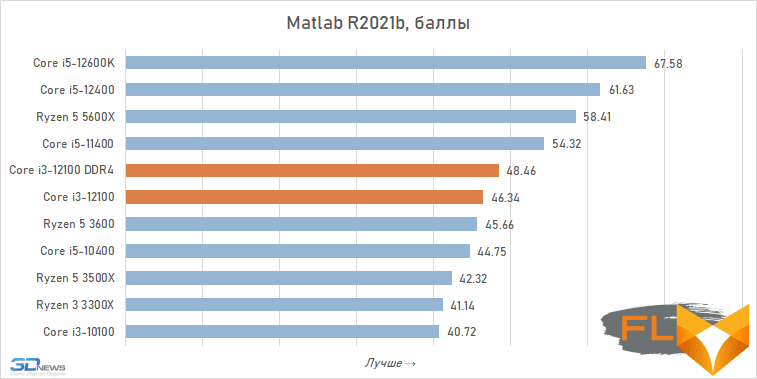
- Mathworks Matlab R2021b (9.11.0) – testing the speed of engineering and mathematical calculations in a popular mathematical package. A standard benchmark is used, which includes matrix and vector operations, the solution of differential and symmetric sparse linear systems of equations, as well as the construction of 2D and 3D plots.
- Microsoft Visual Studio 2017 (15.9.40) – Compile time measurement for a large MSVC project – Blender 2.79b professional 3D package.
- Stockfish 14.1 – testing the speed of the popular chess engine. The speed of enumeration of options in the position “1q6/1r2k1p1/4pp1p/1P1b1P2/3Q4/7P/4B1P1/2R3K1 w” is measured.
- SVT-AV1 v0.8.6 – testing the speed of video transcoding to the promising AV1 format. Performance is measured using a raw 1080p@50FPS AVC video file with a bitrate of about 30 Mbps.
- Topaz Video Enhance AI v2.3.0 – performance testing in an AI-based program to improve video detail. The test uses the original video at 640×360 resolution, which is doubled using the Artemis Anti Aliasing v9 model.
- V-Ray 5.00 – Performance testing of a popular rendering system using the standard V-Ray Benchmark Next application.
- x265 3.5+8 10bpp – testing the speed of video transcoding to H.265/HEVC format. To evaluate performance, we use the original 2160p@24FPS AVC video file with a bitrate of about 42 Mbps.
Games:
- Chernobylite. Resolution 1920 × 1080: Graphics Quality = Ultra.
- Civilization VI: Gathering Storm. Resolution 1920×1080: DirectX 12, MSAA=4x, Performance Impact=Ultra, Memory Impact=Ultra.
- Cyberpunk 2077. 1920 × 1080 resolution: Quick Preset = Ray Tracing – Ultra.
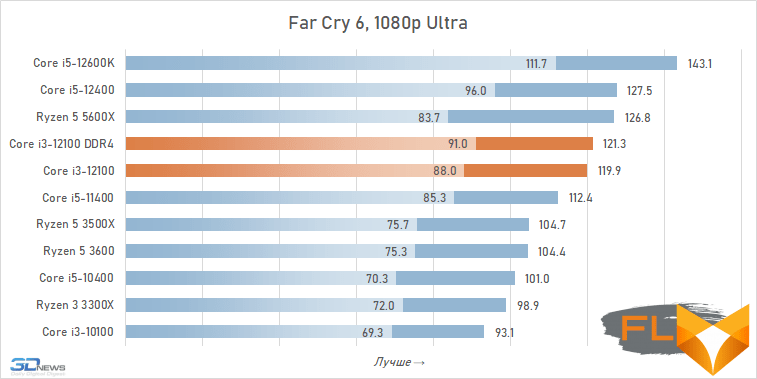
- Far Cry 6. 1920 × 1080 resolution: Graphics Quality = Ultra, HD Textures = On, Anti-Aliasing = TAA.
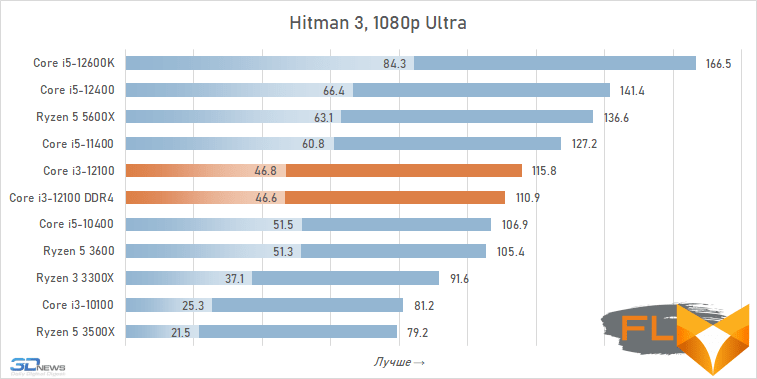
- Hitman 3. 1920 × 1080 resolution: Super Sampling = 1.0, Level of Detail = Ultra, Texture Quality = High, Texture Filter = Anisotropic 16x, SSAO = Ultra, Shadow Quality = Ultra, Mirrors Reflection Quality = High, SSR Quality = High, Variable Rate Shading = Quality.
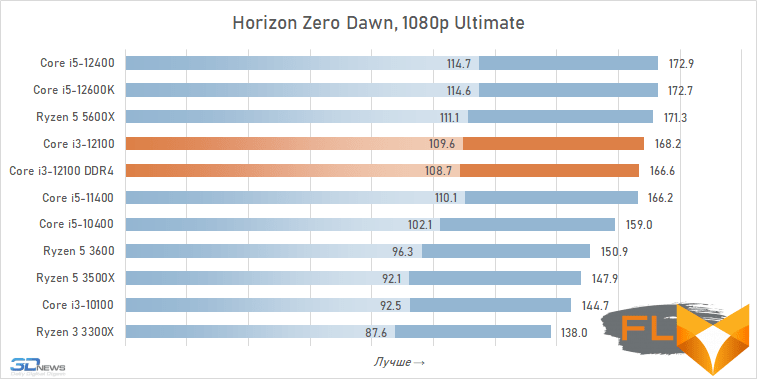
- Horizon Zero Dawn. Resolution 1920 × 1080: Preset = Ultimate Quality.
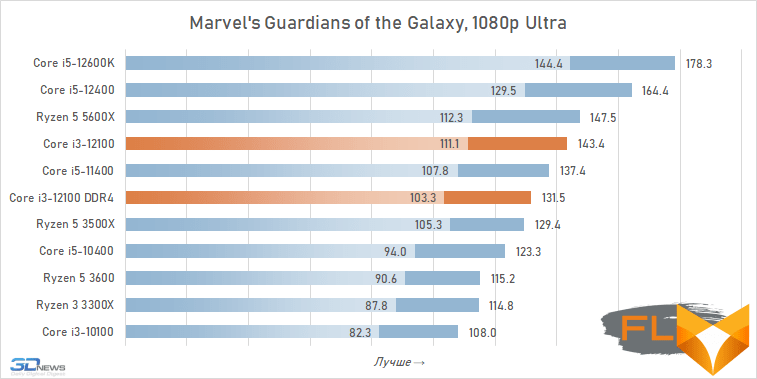
- Marvel’s Guardians of the Galaxy. Resolution 1920 × 1080: Graphics Preset = Ultra.
- Serious Sam: Siberian Mayhem. Resolution 1920 × 1080: Direct3D 11, CPU Speed = Ultra, GPU Speed = Ultra, GPU Memory = Ultra.
- Shadow of the Tomb Raider. Resolution 1920 × 1080: DirectX12, Preset = Highest, Anti-Aliasing = TAA.
- The Riftbreaker. Resolution 1920 × 1080: DirectX12, Texture Quality = High, Raytraced soft shadows = On, Ray traced shadow quality = Ultra, Raytraced ambient occlusion = On.
- A Total War Saga: Troy. Resolution 1920 × 1080: DirectX 12, Quality = Ultra, Unit Size = Extreme.
- Watch Dogs Legion. Resolution 1920 × 1080: DirectX 12, Quality = Ultra, RTX = Off, DLSS = Off.
In all gaming tests, the results are the average number of frames per second, as well as the 0.01-quantile (first percentile) for FPS values. The use of the 0.01-quantile instead of the minimum FPS is due to the desire to clean up the results from random bursts of performance that were provoked by reasons not directly related to the operation of the main components of the platform.
⇡#Performance in complex benchmarks
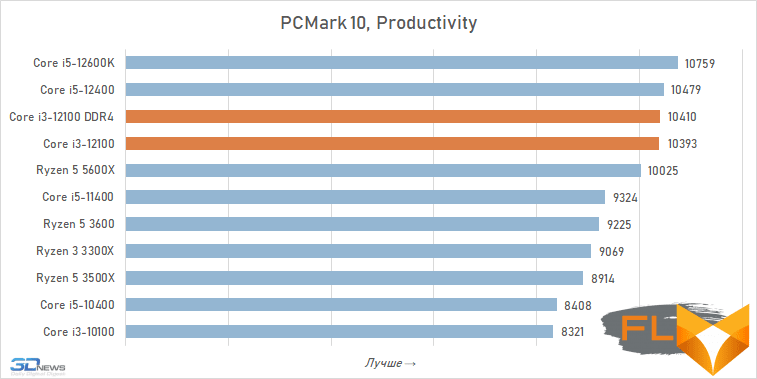
We start testing all processors with testing in PCMark 10 – this benchmark allows you to understand how they cope with normal daily work in common applications. And the results obtained give no reason to doubt the progressiveness of the Core i3-12100. Like other representatives of the Alder Lake family, this processor has excellent single-threaded performance, so that in office and Internet applications, the system based on it demonstrates better responsiveness than systems based on processors of older families.
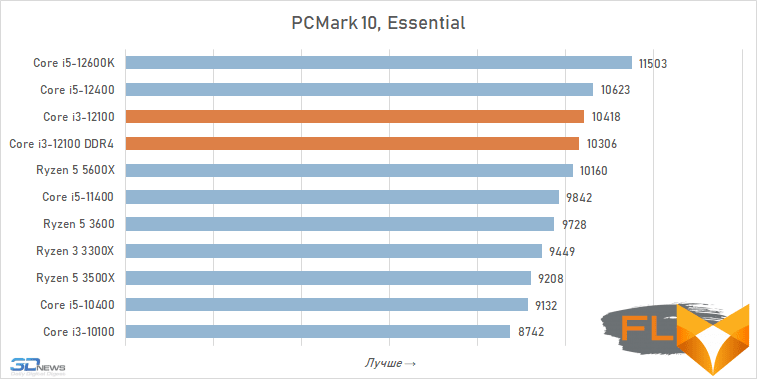
But in the PCMark 10 Digital Content Creation scenario, the situation is slightly different. It talks about speed when creating and processing digital content, and in this case, the six-core Ryzen 5 5600X looks more interesting than the Core i3-12100. But at the same time, the six-core Core i5-11400, and even more so the Core i5-10400, cannot beat the quad-core Alder Lake.
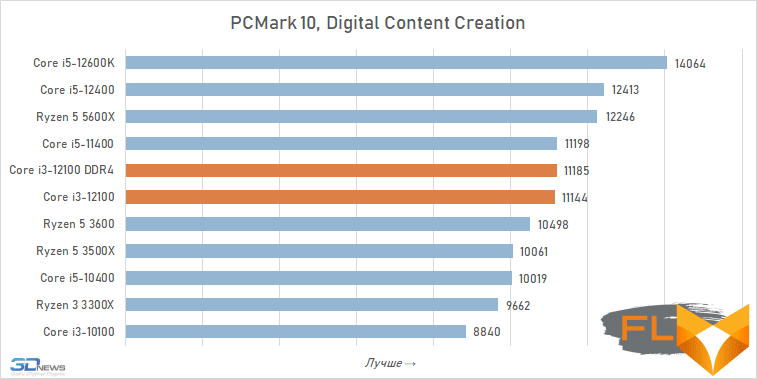
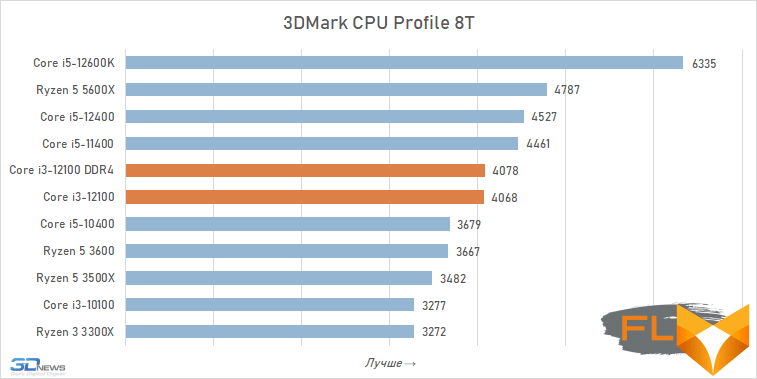
A somewhat different picture is drawn by the near-game 3DMark CPU Profile test. It simulates a certain reference game environment (the physical environment and the actions of abstract non-game characters) using the multi-threaded capabilities of processors. In this case, the Core i3-12100 loses to a larger number of rivals. In fact, any six-core processors turn out to be faster than a quad-core Alder Lake, with the exception of the Ryzen 5 3500X, in which SMT support is disabled. And even if the load is artificially limited to eight threads, the Core i3-12100 still loses to both the Ryzen 5 5600X and the Core i5-11400.
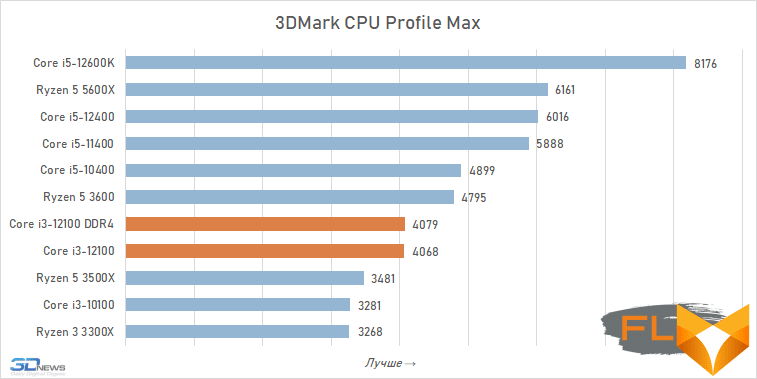
The moral here is very simple: in workloads that involve parallelization, six old cores are better than four new ones, and Golden Cove’s microarchitectural superiority is not enough for the Core i3-12100 to be able to compete on equal terms with the younger six-core AMD and Intel processors of the past generation.
⇡#Performance in Applications
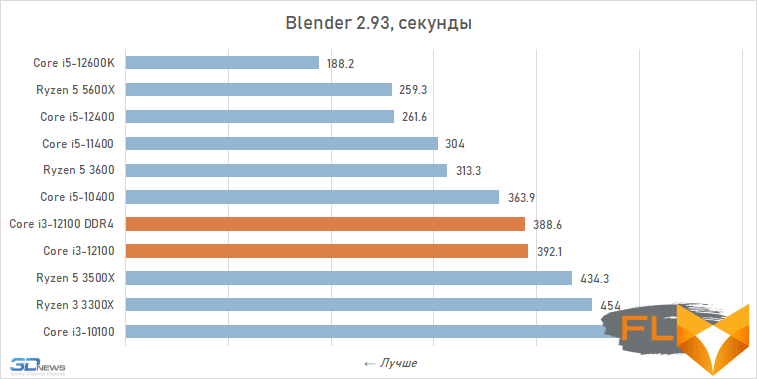
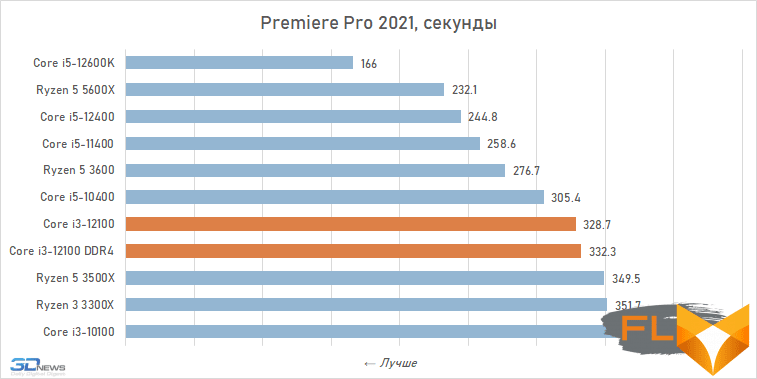
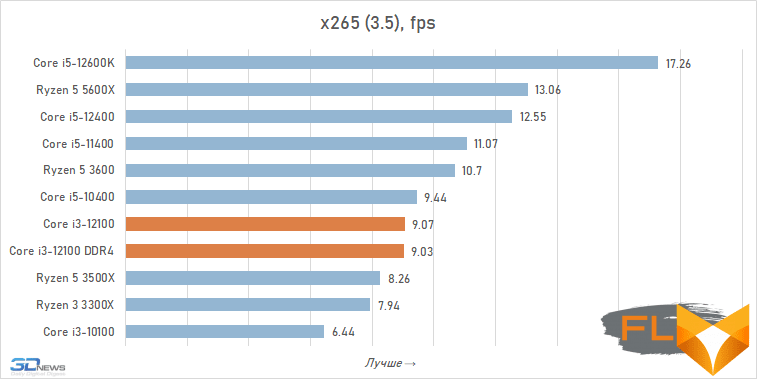
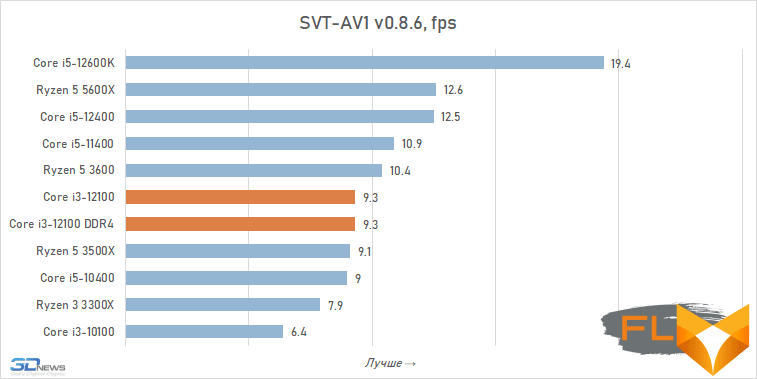
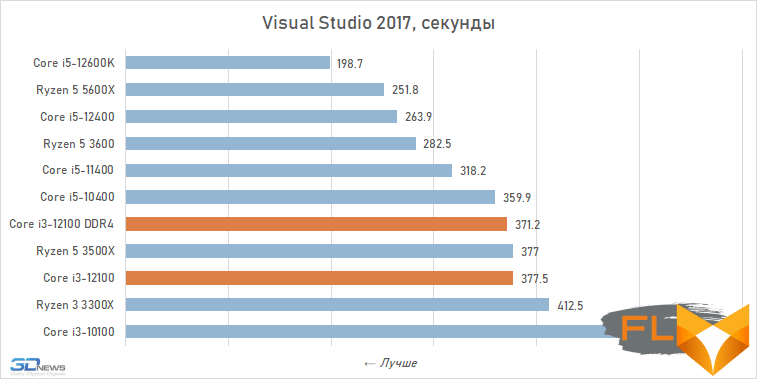
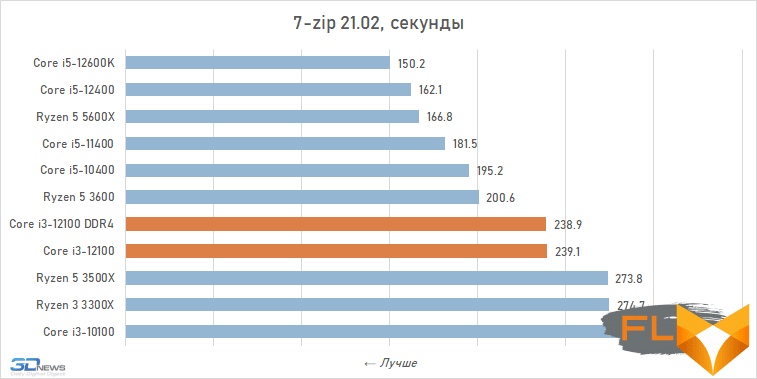
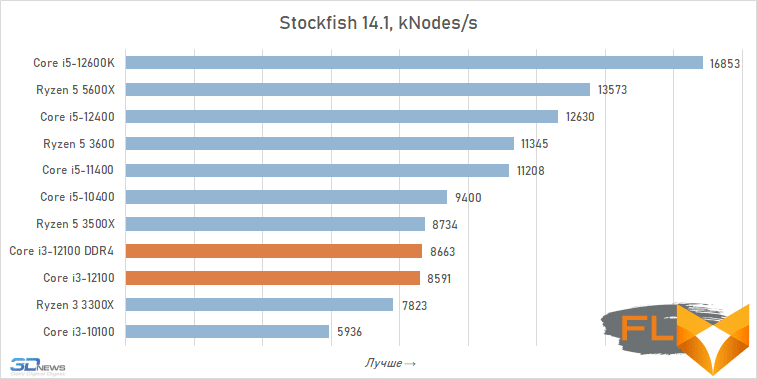
When looking at the performance of the Core i3-12100 in resource-intensive applications, its noticeable superiority over the previous junior Intel quad-core processor, the Core i3-10100, immediately catches the eye. Although these CPUs have similar clock speeds and are capable of executing eight threads simultaneously, the Alder Lake family member is about a third faster. Moreover, this advantage is mainly due to a more modern microarchitecture, and not, for example, support for DDR5 SDRAM, since, as tests show, the Core i3-12100 almost does not benefit from fast new-generation memory.
However, such a performance increase for a qualitative breakthrough is still not enough. The Core i3-12100 is slower than six-core processors based on the older Cypress Cove, Skylake, Zen 3, and Zen 2 microarchitectures. Intel’s budget processor is noticeably inferior. And this means that, despite everything but, in its weight category, the Core i3-12100 is a very strong offer.
Rendering:
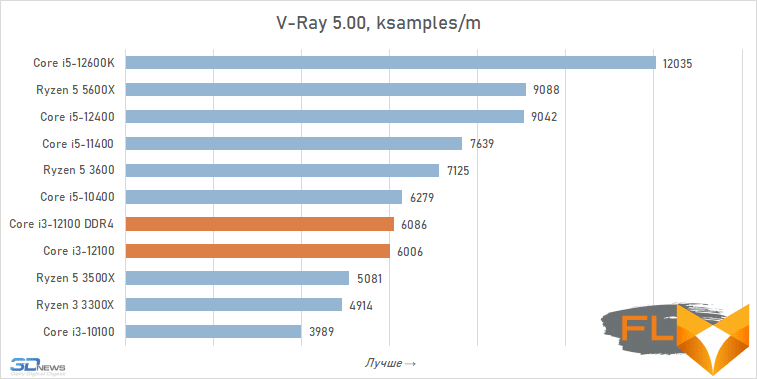
Photo processing:
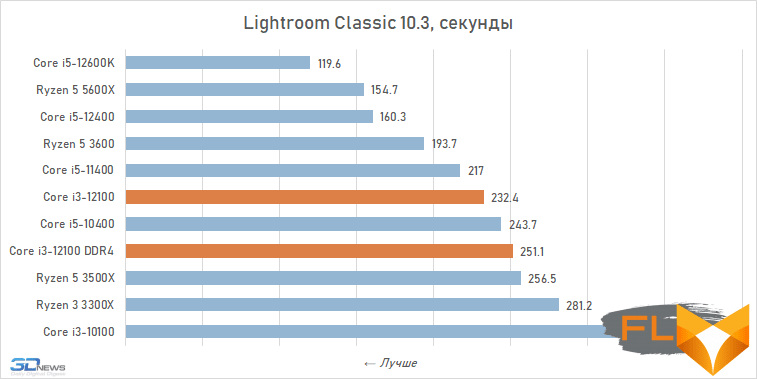
Video work:
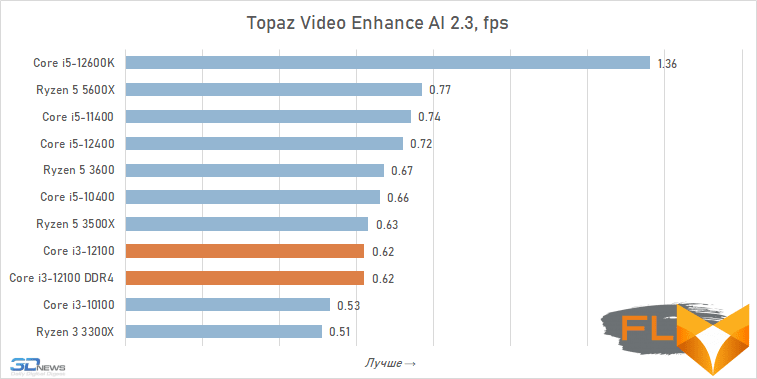
Video transcoding:
Compilation:
Archiving:
Chess:
Mathematical calculations:
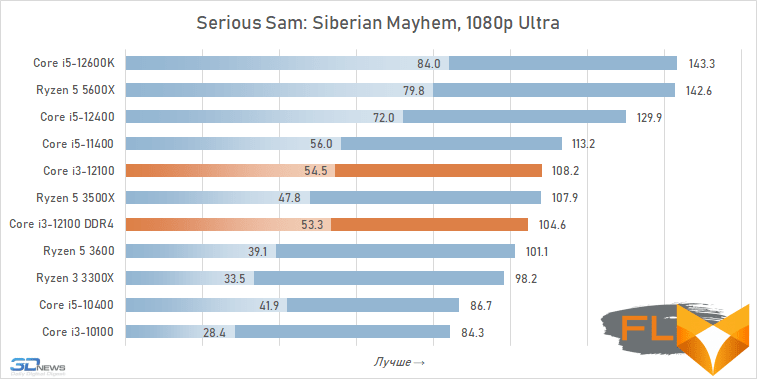
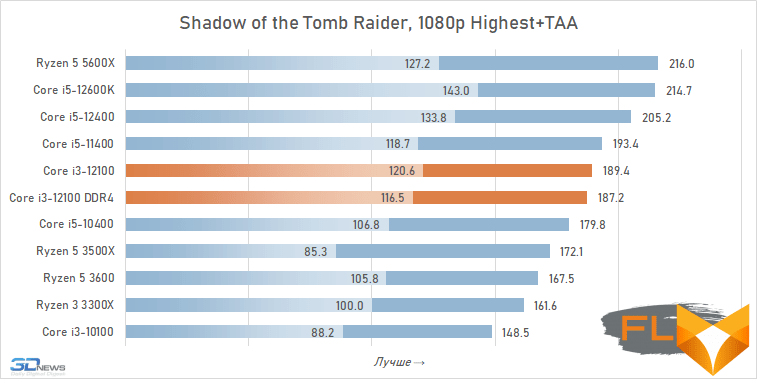
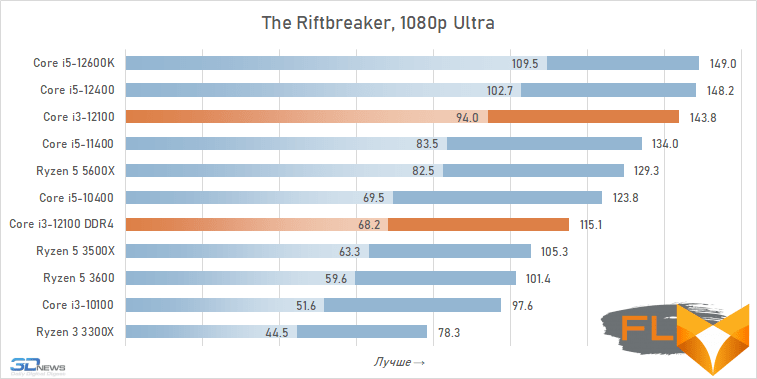
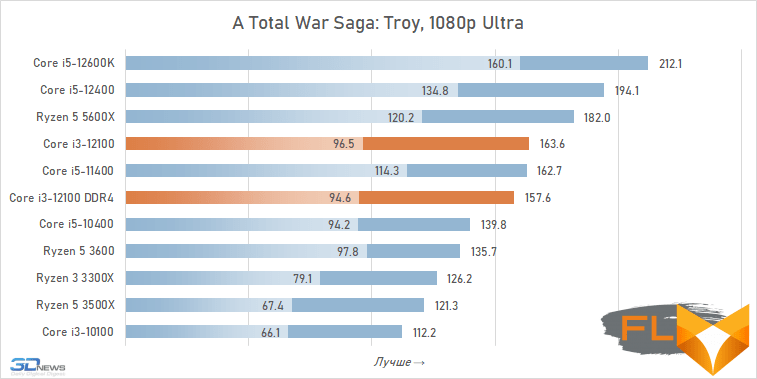
⇡#Game performance
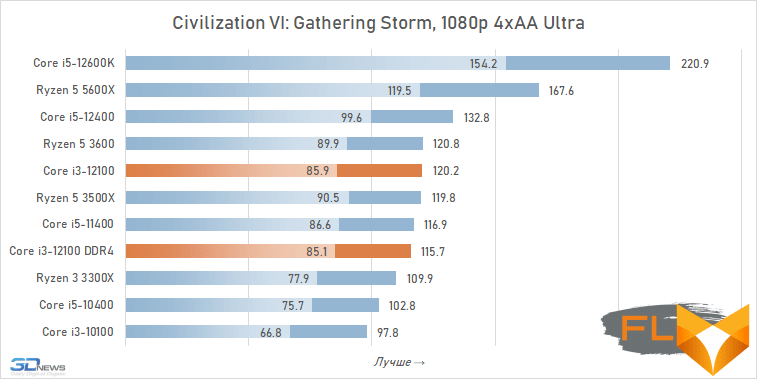
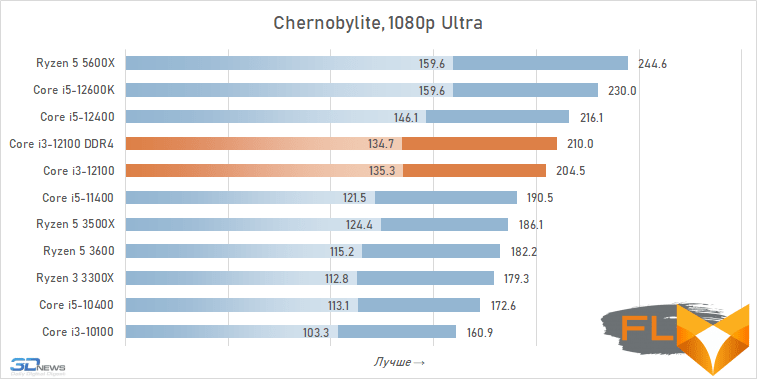
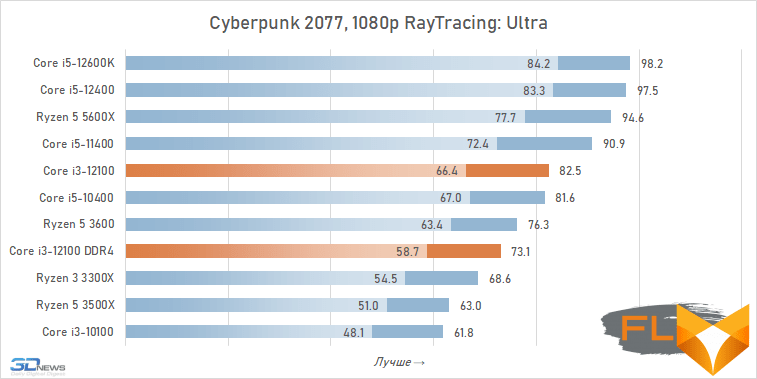
The use of a processor with four processing cores in a modern gaming system is somewhat of a compromise solution. There are more and more games among modern games that get a noticeable gain when moving from four to six cores, and the Golden Cove microarchitecture is not always able to compensate for the lack of parallelism in the Core i3-12100. That is why in some cases the best frame rate can be provided not by the main character of the review, but by the Core i5-11400 of the Rocket Lake generation. However, in fairness, it should be noted that there are no cases where the Core i3-12100 loses in frame rate to the older six-core core i5-10400. In addition, its gaming performance looks better than the “people’s” Ryzen 5 3600X can offer, which opens up good prospects for the Core i3-12100, especially in light of its relative cheapness.
In other words, the general rule for choosing a processor for a low-cost gaming system looks like this: the new Core i3-12100 is faster than older processors with six cores from 2019 – early 2020, but worse than the six-cores of the previous generation of the Rocket Lake and Zen 3 families. This principle extends to use cases Core i5-12100 with both DDR5 and DDR4, but more modern memory can increase average FPS by about 5%.
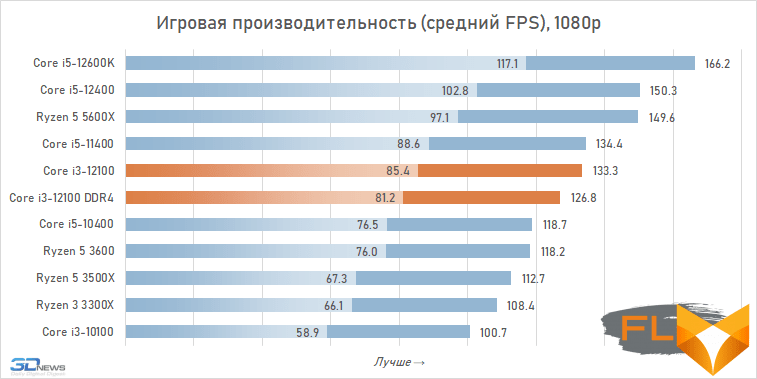
At the same time, if we compare the gaming performance of the quad-core Core i3-12100 with the performance of the six-core Core i5-12400, then the lag of the younger processor does not seem catastrophic at all. Two additional cores add only about 12% to the average FPS level. True, there are separate games where the gap is much more serious. These include, for example, Cyberpunk 2077, Hitman 3, Serious Sam: Siberian Mayhem and Watch Dogs Legion.
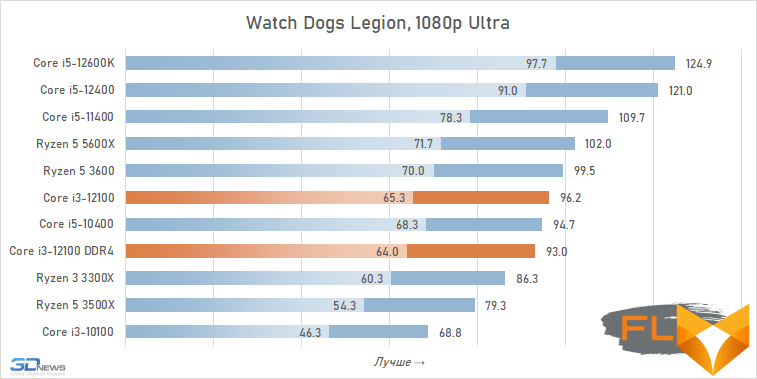
⇡#Conclusions
Most enthusiasts regard the Core i3 processors as compromise solutions, which should be seriously considered only when the budget allocated for the assembly of the system is seriously limited. However, in today’s realities, everything is far from being so, and the Core i3-12100 can hardly be called a cheap option. But this does not make it unattractive, since it is still impossible to buy anything more affordable and better in terms of performance: the Core i3-12100 is head and shoulders above all quad-core alternatives on the market. In applications, it is faster than the Ryzen 3 3300X by at least 15% and faster than the Core i3-10100 by at least 35%. In games, the level of superiority over the quad cores of past generations is even more significant.
At the same time, despite the fact that the Core i3-12100 is one of the processors with a progressive architecture of Alder Lake cores, it is far from always possible to oppose it to six-core solutions of past generations. So, the Core i5-11400 and Ryzen 5 5600X from a year ago are clearly faster than the Core i3-12100, both in resource-intensive tasks and in some modern games, which, like applications for creating and processing content, are no longer always ready to be content with four cores. Therefore, if you close your eyes to the question of price, then when choosing between the Core i3-12100 and the younger six-core Zen 3 and Rocket Lake families, the latter are still preferable.
However, when comparing the Core i3-12100 with the earlier Core i5-10400 and Ryzen 5 3600, things are no longer so clear. Six cores with older microarchitectures may perform better in solving resource-intensive tasks for working with media content, but in gaming systems, the modern quad-core Alder Lake is faster.
Obviously, the final decision in favor of this or that processor is always made taking into account the full cost of the platform. And the Core i3-12100 allows you to approach this issue with enviable flexibility. It can be used with DDR4 memory, which, if it limits its performance, is not too noticeable. In addition, the energy efficiency of the Alder Lake processor design makes it possible to equip the Core i3-12100 with both “budget” LGA1700 motherboards based on the H610 system logic, and rather unassuming cooling systems.
Ultimately, based on the Core i3-12100, it is quite possible to assemble a configuration that does not require any sky-high financial investments, but at the same time, thanks to four full-fledged cores with the fastest microarchitecture at the moment, Golden Cove will cope well with everyday tasks and games. In addition, the system on the Core i3-12100, with a good combination of circumstances, can be upgraded in the future – the LGA1700 platform will not lose its relevance for a long time.